Planet
What Do Cement People Do in the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, "cement people" play a vital role. They are the backbone of building infrastructures. According to the Global Cement and Concrete Association, the cement industry represents about 8% of global CO2 emissions. This figure highlights the need for sustainable practices among cement manufacturers.
Cement people are involved in various aspects of production and application. They manage processes from extracting raw materials to developing innovative formulations. The World Cement Association reports that global cement consumption is projected to reach 5.2 billion tons by 2025. This underscores the significant demand for skilled professionals in this field.
Yet, challenges abound. The industry faces pressure to adopt greener technologies. Innovations are often slow to implement. There’s room for improvement in reducing waste and enhancing sustainability. Cement people must reflect on their practices to drive change. Balancing efficiency and environmental responsibility is crucial for future growth.

The Role of Cement in the Construction Industry
Cement plays a crucial role in the construction industry. It is one of the main ingredients of concrete, which makes up a significant part of building projects. According to industry reports, cement usage has increased by over 60% in the last two decades. This rise highlights cement's essentiality in infrastructure development.
In construction, cement is not just about strength. It also contributes to sustainability. Eco-friendly cement options are emerging, aimed at reducing carbon emissions. However, traditional cement production still poses environmental challenges. It accounted for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions in 2021. The need for greener practices is evident but has yet to be fully embraced.
Challenges remain as the industry navigates these changes. Supply chain issues and fluctuating prices can hinder progress. Only through innovative solutions can the sector move forward. Cement professionals must constantly adapt to these realities. The balance between growth and sustainability remains a complex, yet necessary endeavor.
Types of Cement and Their Specific Applications
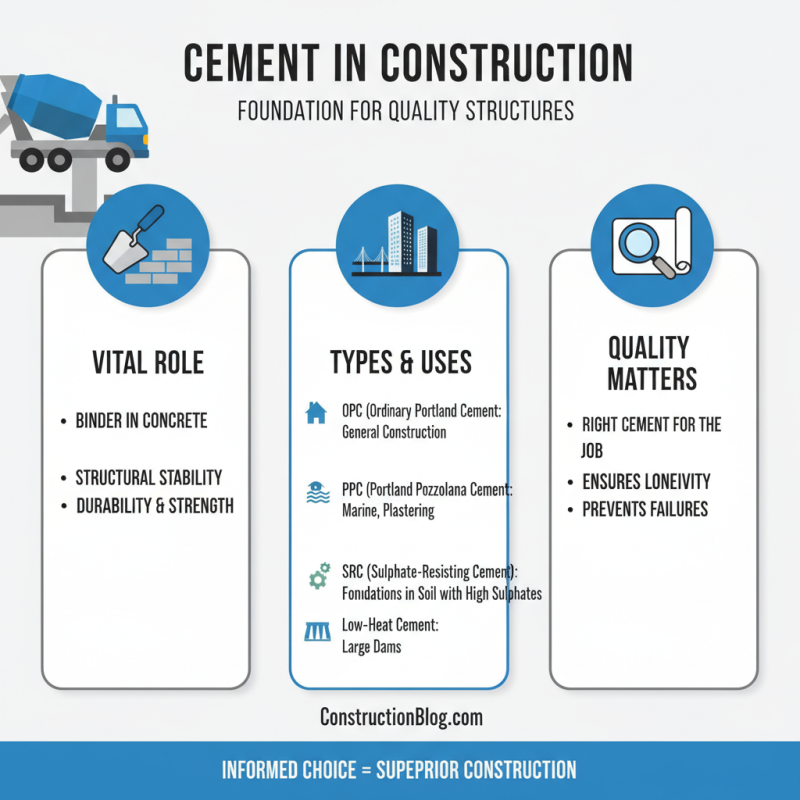
Cement plays a vital role in the construction industry. Various types of cement serve distinct purposes. Understanding these differences is essential for quality construction.
Portland cement is the most common type. It's used in concrete for buildings and roads. This cement hardens quickly and is durable. Another type is masonry cement, used for brick and stonework. It's specially formulated to enhance bonding.
Tips: Always consider the application. Different projects require different cement types.
There’s also sulfate-resisting cement. This type protects structures in environments with high sulfates. Some structures may fail due to incorrect cement choice. Reflecting on past projects can provide valuable lessons here.
Tips: Research local conditions. Match the cement to environmental needs. Always consult with experts for the best option.
Key Processes Involved in Cement Production
Cement production involves several key processes that are vital to the construction industry. The journey starts with raw materials such as limestone and clay. These materials are crushed and blended efficiently. This mixture is then heated in a kiln to produce clinker. The kiln operates at extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1400°C.
After the clinker is formed, it is cooled and ground into powder. This powdered form creates cement. At this stage, many quality checks are performed. Anything less than standard must be discarded. Not every batch comes out perfect, and that can be an issue for production timelines.
Tips for Quality Control: Always conduct tests on raw materials before starting. Small inconsistencies can lead to bigger problems later. Monitor the kiln temperature closely to avoid over-burning, which can compromise quality.
Packaging and distribution follow cement production. Each bag must be sealed and labeled correctly. Care is taken to prevent moisture from entering the bags. Improper handling can cause cement to harden prematurely. Adapting to these challenges is crucial for efficiency in the industry.
The Importance of Cement Quality Control
Cement quality control plays a crucial role in the construction industry. It ensures that the materials used are durable and reliable. When cement quality is compromised, structures can suffer. Cracks, weak foundations, and safety hazards often arise from poor-quality cement. This makes rigorous testing essential.
Testing has many facets. It includes checking for purity, consistency, and strength. Often, quality control involves sampling cement from batches and testing it in laboratories. Some concrete mixtures may not yield expected results despite using standard cement. This is a concerning issue.
Even experienced professionals can misjudge quality. They might overlook minor flaws, impacting overall project integrity. Regular audits and reviews are needed to avoid these mistakes. While challenges exist, maintaining stringent quality standards can greatly enhance the longevity of construction projects.
What Do Cement People Do in the Construction Industry? - The Importance of Cement Quality Control
| Role | Responsibilities | Quality Control Measures | Importance of Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement Technician | Testing cement samples; conducting material analysis | Regular testing for consistency; testing strength and composition | Ensures structural integrity and safety |
| Quality Control Manager | Overseeing quality assurance processes | Implementing ISO standards; conducting audits | Maintains company reputation and compliance with regulations |
| Production Supervisor | Managing cement production lines | Monitoring production quality; adjusting processes | Ensures efficiency and minimizes waste |
| Laboratory Analyst | Analyzing chemical properties of cement | Performing tests like sieve analysis and hydration | Facilitates product development and innovation |
Cement Industry Trends and Future Innovations
The cement industry is showing promising trends. Innovations are emerging that focus on sustainability and efficiency. New materials are being developed to reduce carbon footprints. For instance, alternative cement can utilize industrial waste. This not only cuts down on emissions but also uses materials that would otherwise go unused. The push for greener solutions is evident.
Tips: Explore local resources. They can often provide recycled materials. Collaborating with nearby businesses can spark new ideas.
Another trend is automation in the cement sector. Robotics are enhancing production lines. This helps in speeding up processes while minimizing manual labor. However, it raises questions about job security. Workforce training will be essential to adapt.
Tips: Keep learning. Embrace new technologies to remain relevant. Upskill with workshops or online courses.
Related Posts
-

Top 5 Benefits of Cement People for Your Construction Projects
-

10 Best Ways Cement People Build Strong Community Connections?
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Cement Maker for Your Construction Needs
-

2025 Top Trends in Mixed Concrete: Innovations Driving 10% Industry Growth
-

10 Essential Tips for Using Cement at Home Like a Pro
-
How to Use Cement at Home for DIY Projects and Renovations

- The Monarch Cement Company
- 449 1200 Street
Humboldt, KS
66748 - (620) 473-2222
- sale@rileydesignbuild.com

