Planet
What is Standard Concrete? Key Properties and Uses Explained
Standard concrete is a fundamental building material that serves as the backbone of modern construction. It is a versatile mixture composed of cement, water, sand, and aggregates, which together create a durable and robust substance. According to Dr. Robert Greenfield, a renowned expert in civil engineering and concrete technology, “Standard concrete is essential for providing the strength and longevity required in structural applications.” This assertion underscores the critical role that standard concrete plays in ensuring the safety and stability of various infrastructures, from residential buildings to bridges.
The properties of standard concrete, such as compressive strength, workability, and durability, make it an invaluable resource in the construction industry. Its ability to withstand heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions makes it a preferred choice for both structural and decorative applications. Additionally, the ease of mixing and molding standard concrete allows for flexibility in design, catering to the diverse needs of architects and builders. Therefore, understanding the key properties and uses of standard concrete is crucial for anyone involved in construction, whether as a professional or a homeowner embarking on a renovation project. Through exploring these attributes, we can appreciate how this material has become a cornerstone of the built environment.

What is Standard Concrete: An Overview of Its Definition
Standard concrete is a widely used construction material composed of a mixture of cement, aggregates (sand and gravel), and water. This versatile material is primarily defined by its compressive strength, which typically ranges from 20 to 40 MPa (megapascals), making it suitable for a multitude of structural applications. According to the American Concrete Institute, standard concrete accounts for approximately 75% of the total concrete used in construction projects, emphasizing its prominence in the industry.
The properties of standard concrete set it apart as a reliable building material. Its durability, resistance to weathering, and ability to withstand heavy loads make it an ideal choice for infrastructure projects, pavements, and building foundations. Research indicates that concrete can maintain its integrity for over 50 years under proper conditions, with minimal maintenance required. In addition, the thermal mass properties of standard concrete help in energy efficiency, reducing heating and cooling demands in buildings. As urbanization continues to rise, the demand for standard concrete is projected to grow, with global market size expected to reach USD 1,031.6 billion by 2027, according to industry reports.
What is Standard Concrete? Key Properties and Uses Explained
| Property | Description | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | The ability of concrete to withstand axial loads without failing. | Pavements, foundations, and structural components. |
| Durability | Resistance to weathering, chemical attack, and abrasion. | Bridges, highways, and marine structures. |
| Workability | Ease of mixing, transporting, placing, and finishing. | Residential and commercial construction projects. |
| Water-Cement Ratio | The ratio of water to cement in a concrete mix impacting strength and durability. | All concrete applications, especially in structural design. |
| Thermal Properties | Ability to absorb and retain heat. | Building envelopes, thermal mass applications. |
Key Properties of Standard Concrete: Strength, Durability, and Workability
Standard concrete is a pivotal material in the construction industry, prized for its key properties of strength, durability, and workability. Its compressive strength, typically ranging from 20 MPa to 40 MPa, makes standard concrete suitable for a variety of structural applications. This strength is essential for bearing loads in buildings, bridges, and roads, where robust performance is non-negotiable. According to the American Concrete Institute (ACI), higher strength concrete variants can even exceed 80 MPa, showcasing how advancements in technology continue to enhance the material's capabilities.
Durability is another intrinsic property of standard concrete, making it a reliable choice for long-term constructions. It exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, chemical attacks, and abrasion, ensuring longevity in diverse environments. Research conducted by the National Ready Mixed Concrete Association highlights that properly designed and cured standard concrete can last over 50 years with minimal maintenance. This characteristic is crucial for infrastructure projects, where the cost of repairs can be significant.
Workability, defined by how easily concrete can be mixed, placed, and finished, is vital for achieving desired shapes and finishes in construction. Standard concrete can achieve an optimal balance between cohesion and fluidity, allowing it to flow efficiently into molds without segregation of materials. According to the Portland Cement Association, this adaptability ensures that workers can manipulate mixtures to meet specific project requirements, whether for structural or decorative purposes. Consequently, the triad of strength, durability, and workability establishes standard concrete as a foundational material in modern construction practices.
Common Applications of Standard Concrete in Construction and Infrastructure

Standard concrete, a widely utilized building material, plays a vital role in various construction and infrastructure projects. Its versatility allows it to be employed in applications such as roadways, bridges, and foundations. According to the American Concrete Institute, concrete is the most consumed man-made material globally, with approximately 10 billion tons produced each year, which underscores its significance in modern construction.
One of the key applications of standard concrete is in the construction of pavements. A report from the Portland Cement Association indicates that concrete pavements have a life expectancy of over 30 years with proper maintenance, making them a durable choice for urban development. Additionally, standard concrete is frequently used in structural components like beams and columns, providing essential strength and stability to buildings. Its inherent properties, such as compressive strength of up to 4,000 psi, make it ideal for handling heavy loads commonly found in infrastructure projects.
Tips: When working with standard concrete, it’s essential to consider local climate conditions. For example, adding water-reducing admixtures can enhance performance in hotter environments, ensuring the material cures effectively. Furthermore, early finishing techniques can improve surface durability, especially for outdoor installations exposed to varying weather patterns.
Understanding the Composition and Mix Design of Standard Concrete
Standard concrete is primarily composed of four key ingredients: cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures. Cement acts as the binding agent, while aggregates—consisting of sand, gravel, or crushed stone—provide bulk and strength to the mix. The water not only hydrates the cement to form a strong bond but also facilitates the mixing process. Admixtures, which are optional additives, can enhance specific properties of concrete, such as workability, strength, or curing time, allowing for customization based on project requirements.
The mix design of standard concrete is critical to achieving the desired properties for various applications. Engineers typically use established guidelines and design methods to determine the optimal ratios of ingredients, considering factors such as load-bearing capacity, durability, and environmental conditions. Common mix designs include proportions by weight or volume, where a typical ratio might be 1:2:3 for cement, sand, and aggregates, respectively. By carefully adjusting these components, standard concrete can be tailored to meet the demands of structural, architectural, and infrastructural projects, ensuring performance and longevity in diverse settings.
Standard Concrete Properties and Compositions
This chart illustrates the key properties of standard concrete, including compressive strength, workability, durability, and water-cement ratio. These metrics are essential in understanding the performance and application of standard concrete in construction.
Maintenance and Performance Considerations for Standard Concrete Structures
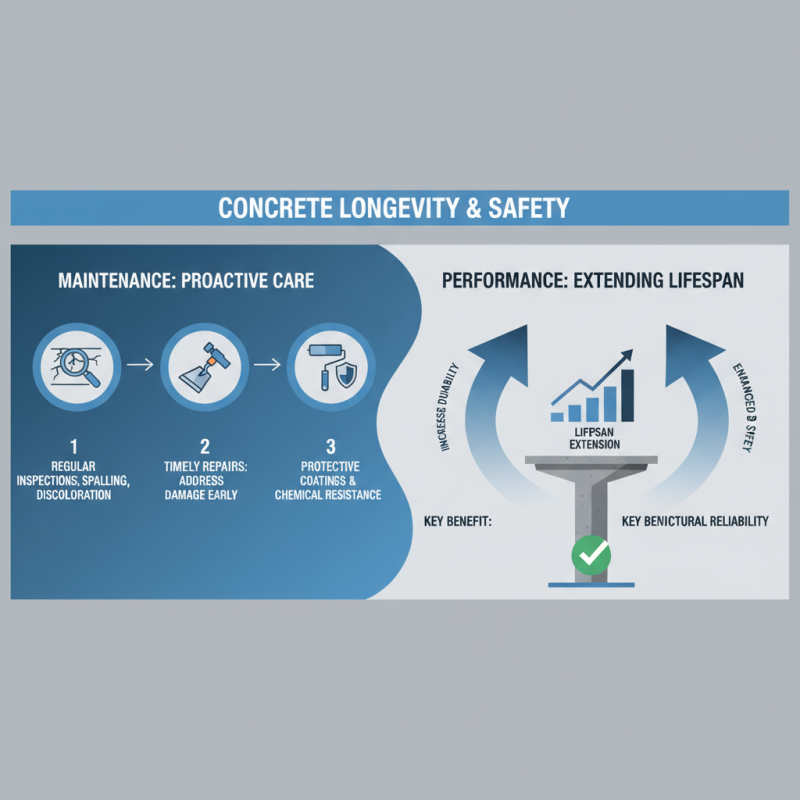
Maintenance and performance considerations for standard concrete structures are critical for ensuring their longevity and safety. One of the primary aspects of maintenance involves regular inspections to identify signs of wear and damage, such as cracks, spalling, or discoloration. These indicators can be early warnings of more severe structural issues. Implementing a proactive maintenance plan that includes timely repairs and protective coatings can significantly extend the lifespan of concrete structures.
Performance under varying environmental conditions is another key factor to consider. Standard concrete is susceptible to deterioration due to factors like freeze-thaw cycles, chemical exposure, and moisture penetration. To enhance durability, using appropriate water-repellent sealers and ensuring proper drainage can mitigate risks associated with water accumulation. Additionally, incorporating additives during the mixing process can improve resistance to these environmental challenges. By addressing these maintenance and performance aspects, practitioners can optimize the use of standard concrete in various applications, ensuring that structures remain resilient and functionally sound over time.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Trends in Mixed Concrete: Innovations Driving 10% Industry Growth
-

How to Increase Concrete Strength: Tips and Techniques for Best Results
-

Top 10 Ready Cement Products to Transform Your Construction Projects in 2025
-

2025 How to Optimize Portland Cement Production for Sustainable Construction
-

How to Choose the Best American Concrete for Your Construction Project
-

Understanding the Benefits of American Concrete in Modern Construction Techniques

- The Monarch Cement Company
- 449 1200 Street
Humboldt, KS
66748 - (620) 473-2222
- sale@rileydesignbuild.com

